In these cases the locomotory organelles are pseudopodia or flagella or both. The protozoa are then placed into various groups primarily on the basis of how they move.

Protozoa Definition Classification Characteristics Structure Diseases Examples
QUESTION 2 Protozoan classification is based on their means of.

. They reproduce primarily by asexual means although in some groups sexual modes also occur. Protozoa are generally distinguished from other eukaryotic protists by their motility and by their lack of cell wall. Protozoan classification used to be based on their means of locomotion.
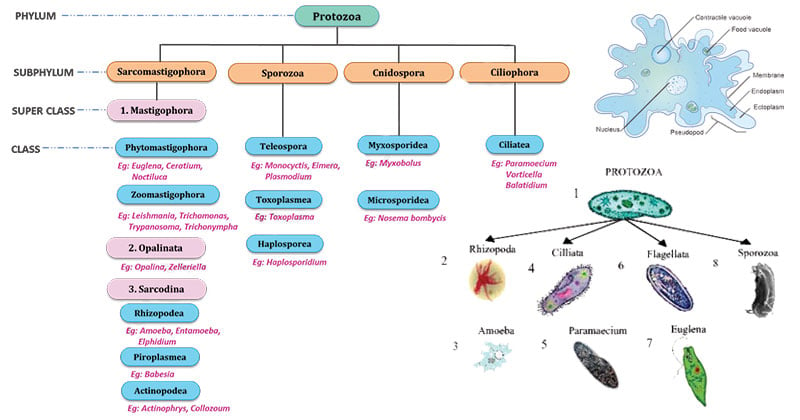
Protozoa can be divided into four phyla based on their locomotion. There are three classes. Another classification is based on the scheme given by the Committee on Taxonomy and Taxonomic Problems of the Society of Protozoologists and mainly proposed by BM Honigberg and others 1964.
They often cause serious diseases such as malaria kalaazar sleeping sickness dysentery etc in their host. The phylum protozoa has been divided into four classes. This means that they are single celled organisms that have a nuclei as well as a number of other important organelles within the cytoplasm and enclosed by a membrane.
Protozoan classification is based on their means of A. They produce carbohydrates or foods from carbon dioxide and water. Some of the members reproduce by asexual mode some by sexual means and some by both.
The classification is based principally on their mode of locomotion. Protozoa reproduce by the method of binary fission or multiple fission. Animal-like protists are commonly called protozoa singular protozoan.
Protozoa species move on their own by one of the three types of locomotor organelles such as flagella cilia or pseudopodia. It divides protozoa into four subphyla. Protozoa are classified into three main category based on their mode of nutrition such as.
They are animal-like because they are heterotrophs and are capable of moving. The protozoa group comprises more than 65000 species. Phylum Protozoa is divided into two subphyla.
How to protozoa operate in the life cycle. Although protozoa are not animals they are thought to be the ancestors of animals. The subkingdom Protozoa is divided into 7 phyla of which 4 mainly Sarcomastigophora Apicomplexa Microspora and Ciliophora have representative that are parasitic.
Previously the protozoan classification was done mainly on the basis of locomotor organs but recently the electron microscopic findings have added new dimension to the study of Protozoa and the scheme of protozoan classification has been changed considerably. They exist as free-living organisms or as parasites. Some protozoa live as unwanted guests or parasites within the body of other animals.
The groups are called phyla singular phylum by some microbiologists and classes by others. Based on ecologyhabitat protozoa can be divided into several categories. Members of the four major groups are illustrated in Figure 1.
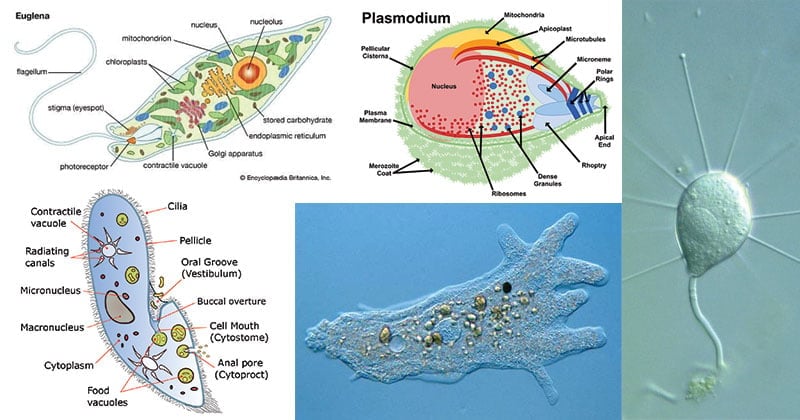
CLASSIFICATION OF PROTOZOA The classification of the protozoa is based on the modified form of that proposed by Levine et. Protozoa is classified by many based on different characters of protozoa but the classification of Protozoa is complicated and difficult The classification followed here is based on Hymans classification. Mastigophora Members of the phylum Mastigophora move about by using one or more whiplike flagella.
The term protozoa originates in the Greek language from the words protos meaning first and zoon meaning animal. This is in reference to their relatively simple morphological structures which. Phylum Protozoa Classification Structure Life Cycle and Microscopy Introduction.
Classification of Protozoa based on the Mode of Nutrition. They are subdivided into the following four. There is presence of one nucleus or more nuclei in organism.
View the full answer. All protozoal species are assigned to the kingdom Protista in the Whittaker classification. As a result protozoology as a field of study is divided into the following categories branches.
An array of protozoa showing. All protozoal species are assigned to the kingdom Protista in the Whittaker classification. Reproduction structure identification growth obtaining nutrients locomotion.
Essentially protozoa are single-celled eukaryotes. Most protozoa consist of a single cell. The protozoa are then placed into various g.
For instance whereas some protozoa can be found living freely in terrestrial environments soil others live as parasites in different animals. Kingdom - Protista Sub-kingdom - Protozoa. The Protozoa are considered to be a subkingdom of the kingdom Protista although in the classical system they were placed in the kingdom Animalia.
Protozoa is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes either free-living or parasitic that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. The following classification is based on Honigberg Report. Protozoa are ecologically important in the food chain of aquatic communities.
Phylum Protozoa is divided into four subphyla based on locomotory organs. Mastigophora Sarcodina Ciliophora and Sporozoa. More than 50000 species have been described most of which are free-living organisms.
Historically protozoans were regarded as one-celled animals because they often possess animal-like behaviours such as motility and predation and lack a cell wall as found in plants. The classification of protozoa is mainly based on their means of locomotion.
Protozoa Definition Characteristics Classification Examples

This Is Paramecium A Member Of Phylum Protozoa Micro Organisms Like Paramecium Eat Other Organisms Or Decaying Parts Of Ot Flashcards Science Passages Science

0 Comments